

Proper orientation of occlusal plane is mandatory for an esthetically and functionally satisfying complete denture. Occlusal plane analysis using android mobile application, utilizing vertical (for midline) and horizontal lines as reference, is used to capture the https://doi.org/10.55231/jpid.2025.v08.i02.07 Introduction photograph of the patient. Images are obtained at a distance of 1m with patient in upright position so that horizontal green line is made to coincide with the ala-tragus line and red line with outer wings of fox plane. The proposed technique is suitable for assessing the midline and nasolabial inclination also. This technique facilitates task of occlusal plane adjustment and orientation an easier and time saving process.
Key words: Ala-tragus line, edentulous, laser level android application, prosthesis
Esthetics, phonetics, mastication and comfort are
the fundamental requirements determining the
long term success of a prosthesis1. Biting force
exerted is greatest when the occlusal plane is
made parallel to the ala-tragus line. It decreases
with a 5 degrees inclination both anteriorly
and posteriorly. Moreover force exertion during
various muscle activity is least when the occlusal
plane is made parallel to the ala-tragus line2.
Many researchers suggested use of superior
border of tragus as the reference point whereas
a few suggested use of middle or inferior point of
tragus for the same3,4. It was Zarb and Bolender,
through their years of research, advocated that
the occlusal plane should be made parallel to
the ala-tragus line if a satisfactory denture is
to be made.5 Many clincians consider the ala-
tragus line as a line running from the superior
border of tragus of the ear to the inferior border
of the ala of the nose.6,7 During routine clinical practice, the occlusal plane is made parallel to
ala-tragal line posteriorly and interpupillary line
anteriorly by repeatedly checking the parallelism
of the occlusal rim with the use of instruments
like fox plane8. Usually a line is drawn on the
face with the help of a thread coated with either
plaster of paris or pumice is taken as a guide
to adjust the occlusal rims in our routine clinical
practice. This possesses the disadvantage of
frequent redrawing of line which is easily erased
during the procedure. Rough visualization of the
ala-tragus line is another method of establishing
parallelism of the wax occlusion rim. It is noticed
that while attempting to stabilize the occlusal
rim, the fox plane and tongue depressor,
the operator evaluate the angulation from a
frequently awkward position as dictated by the
hand held items. Previous methods of evaluating
parallelism of the occlusion rim and ala-tragus
line is often difficult for the operator, especially
while working without assistance. Even when
assistance is available, precise reorientation
of the fox plane and tongue depressor for
comparison of the right and left ala-tragal lines
to the tentative occlusal rim is difficult with the
conventional technique9. These limitations call
for the implementation of an innovative method
for accurate visualization of the occlusal plane.
The purpose of this article is to describe a novel
technique of using an android application for
precise orientation of occlusal plane parallel to
ala- tragal line.
Laser Level Tool 2.0 (Figure 1, John Risch,
Sweden) android application is employed for
orientation of occlusal plane in the patient. This
level tool employed a camera combined with an
accelerometer. It has a vertical and horizontal
line both in red and green colors with provision
for estimating the degree of tilt. The vertical and
horizontal green lines are stationary and are
used as the reference plane. The position of red
lines can be altered by touching the screen of
mobile at the required site. Its orientation can be
altered by tilting the mobile phone.
The patient is made to sit in an upright position
in the dental chair, looking straight ahead and
ala-tragal line parallel to the floor. The maxillary
occlusion rim is gently placed in patient’s mouth
and checked for labial fullness, visibility and lip
support.
The Fox plane (Dentsply International, Trubyte)
is positioned intraorally so that it makes contact
with occlusal rim uniformly. Inferior border of
ala of nose and the middle margin of tragus
were marked on the patient for occlusal plane
determination.
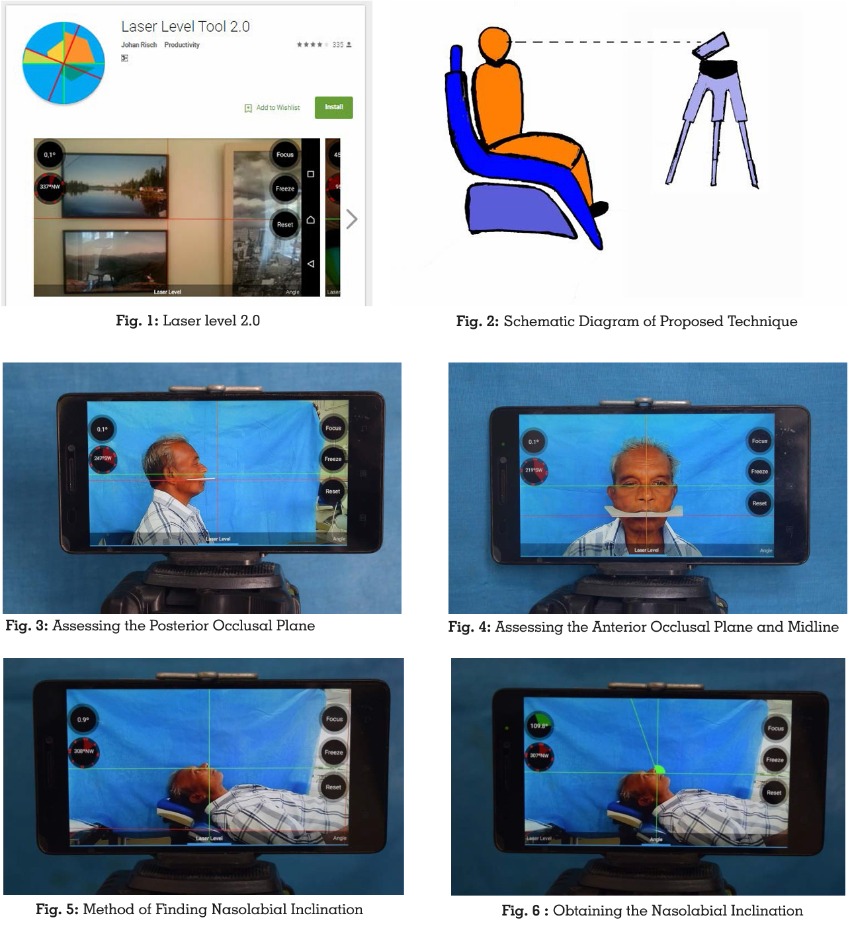
Using an adjustable tripod the height of mobile
(Lenovo A7000 Lenovo CHINA), was adjusted
according to the patient. Photographs were
taken from a fixed distance of one metre from
patients mid sagittal plane with subjects with
their back straight. (Figure 2)
Photographs were made in such a manner that
the horizontal green line coincided with the line
joining the middle margin of tragus to inferior
border of ala of nose and the tilt showed zero
degree. A zero degree on the mobile app implies
parallelism to the floor. The position of red line
can be altered by touching the screen at the
desired position.
Once the photograph is taken, the horizontal red
line is made to coincide with outer wings of the fox plane. Thus degree of tilt and parallelism
can be assessed from the photograph. Using the
green line as a guide the occlusal plane can be adjusted in the conventional manner to attain
the desired parallelism (Figure 3).
Another photograph with the vertical green line passing through the midline of the patient
and horizontal green line coinciding with the
interpupillary line was taken to assess the
midline and also the parallelism of occlusal
plane anteriorly (Figure 4).
The nasolabial inclination can be recorded by
making the patient positioned in supine on the
dental chair with ala-tragal line perpendicular to
floor. Photograph was made with the horizontal
green line passing through the philtrum of upper
lip and with the point of intersection of the 2 lines
coinciding with the junction of philtrum and base
of nose (Figure 5). The angle can be recorded
by simply placing a line at the desired position
(Figure 6).
The conventional techniques described earlier
are prone to errors as the line is drawn on
the soft tissue of the face and is likely to be
smudged, which result in faulty orientation of
occlusal plane. Compared to the conventional
methods, the technique proposed here is ideal
for reorientation and comparison of right and
left ala-tragal lines and is a boon while working
without assistance. Lenovo A 7000 mobile
camera with a resolution of 8 Mega pixels, which
is more than adequate for photographic analysis
is employed. The in-built zoom lens with an auto
focus range to infinity ensured that the image
were of high quality. The camera was placed on
a standard adjustable tripod stand. The arms
and adjustable plates of the tripod stand were
set so that mobile was parallel to the horizontal.
[10] The perpendicular distance between the
subject’s sagittal plane and photographic
film was 1.0 meter.11 In the present technique
photographs were taken at a zero degree tilt.
A 0o indicates that the apparatus is parallel to
the floor. Further, the parallelism between the
horizontal green and red lines are analysed
at 0o and the occlusal rims can be adjusted accordingly using the photographs obtained.
The nasolabial angle can also be derived
precisely from this mobile application, which will
act as a reference guide in determining fullness
of maxillary denture.
The method presented in this article provides a
more reliable, reproducible and stable alignment
of the occlusal plane to the ala-tragal line than
rough visualization. This enables the dentist
to simply and quickly establish a well-defined
starting point in orientation of occlusal plane in
complete denture fabrication. It possesses the
following advantages like cost effectiveness,
patient friendliness as the apparatus is used
outside the mouth. It can be used in patients
with facial deformity like in cases of absence of
an eye and an ear. It provides a new means of
marking the reference plane. It also reduces the
need of multiple reinsertion of fox plane in the
patient’s mouth since the photograph obtained
can be used as a guide to adjust the occlusal rim
in the laboratory.
The proposed technique provides a more
reliable, stable and reproducible orientation
of occlusal plane. It also allows for easy
visualization of the facial midline and can also
be used to determine the nasolabial angle.
Since the procedure is standardized it allows
for easy reorientation. Moreover it can be used
for adjusting the occlusal plane in patients with
facial disfigurements.
CONFLICT OF INTEREST:
None declared