

Introduction: Resilient lining materials are used
on dental prostheses to aid in the distribution of
functional loads to the denture bearing areas,
to avoid localised stress concentrations, and to
improve retention by engaging undercuts. The
major requirements for long-term, resilient liners
are permanent resiliency, high dimensional
stability, good adhesion to the denture base,
adequate tear resistance and compatibility with
oral tissue. The material which increases in hardness
during use, loses its therapeutic properties.
Aim: To compare the difference between the change
in hardness in two silicone-based denture reliners
after storing in artificial saliva in different time
period.
Methodology: Two commercially available
silicone-resilient denture reliners were tested in
this comparative in vitro study: Elite soft Relining;
Zhermack SpA, GC Reline Soft; GC Corp. Specimens
were prepared using metal moulds and stored in artificial saliva and the measurement were taken with
Shore A durometer in a period of 1month, 6months
and 1 year and the mean was compared.
Conclusion: Elite relining material is proved to
have greater hardness than Mollosil but both the
materials have hardness within the limit of required
hardness of long term soft denture liner (LTSDL).
b. Elite and Mollosil did not increase their
hardness when studied at different time period
and this property of stability in hardness overtime
is beneficiary for a LTSDL.
Key words: Geriatric dentistry, Oral health, Denture reliners, long term lining, soft lining materials, silicon based lining, gerodontology
Removable prosthodontics is concerned with
replacing the teeth and soft tissues with a
prosthesis that can be removed. These are
often known as dentures, and can replace a full arch of teeth (complete dentures), or a number
of individual or grouped tooth spaces (partial
dentures).1 There is, inevitably, the potential for
problems to arise subsequent to the insertion
of complete dentures which may be transient
and be essentially disregarded by the patient
or they may be serious enough to result in the
patient being unable to use the dentures.2 The
relining of complete dentures involves solving
the problems encountered in the construction of
new dentures, except positioning the individual
teeth.3 Denture relining is defined as procedure
used to resurface the tissue side of denture.4
Resilient lining materials are used on dental
prostheses to aid in the distribution of functional
loads to the denture bearing areas, to avoid
localized stress concentrations, and to improve
retention by engaging undercuts.5 They have
the potential of improving comfort to denture
patients with ridge atrophy, thin and non
resilient mucosa, bony undercuts, in cases of
irregular bone resorption, immediate prosthesis,
healing after implant placement, and for
patients with bruxism and xerostomia.6 Based
on their chemical structure, soft lining materials
can be acrylic-based and silicone based liners.
Although acrylic-based soft denture liners
exhibit better viscoelastic properties, they have
disadvantages such as unpleasant odor and
taste, and irritation to the soft tissue inside
the mouth. These drawbacks are caused by
the monomer contained in acrylic-based soft
denture liners. On the other hand, silicone
based denture liners have often been used on a
longterm basis because they are more resilient
and more resistant to aged deterioration than
acrylicbased denture liners.6
The major requirements for long-term, resilient
liners are permanent resiliency, high dimensional
stability, good adhesion to the denture base,
adequate tear resistance and compatibility
with oral tissue.7 The material, which increases
in hardness during use, loses its therapeutic properties. The appropriate degree of hardness
and its stability over time is significant clinical
importance and determines the period in which
relining performs its therapeutic role. In this in
vitro study change in hardness of two different
silicone based denture reliner stored in artificial
saliva at different time intervals are compared.
Two commercially available silicone resilient
denture reliners were tested in this comparative
in vitro study: Elite soft Relining; Zhermack SpA,
Mollosil soft relining material.8
SAMPLE SIZE: Sample size for this study is
calculated from the formula using Nmaster
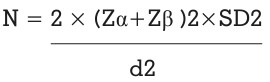
S1= Standard deviation in the hardness of Elite
at 1 month=2.5; S2=Standard deviation in the
hardness of Mollosil at 1 month=2.9 (9)
(Alpha error (%) =5, Power (%) =80, SD=3.9,
Mean Difference=3.2); Sample Size = 11 per
arm The hardness of materials is determined
by Shore method using an instrument called
a durometer which measures the penetration
depth in the material created by a given force
on a standardized presser foot.10 Pilot testing
of specimens revealed that to obtain objective
results using a Shore A durometer, the specimen
thickness should be at least 6 mm and all
measurements should be performed at least
12 mm from their edges. For Shore A hardness
examination, disk-shaped specimens were
prepared with a base diameter of 40 mm and a
height of 8 mm using metal moulds and stored
in artificial saliva and the measurements were
taken in a period of 1 month, 3 months and
6months and then the mean were compared.
(Fig 1 to 5)

Two commercially available silicone resilient
denture reliners (Elite soft Relining; Zhermack
SpA, Mollosil soft relining material) were tested
for hardness at different time periods in this
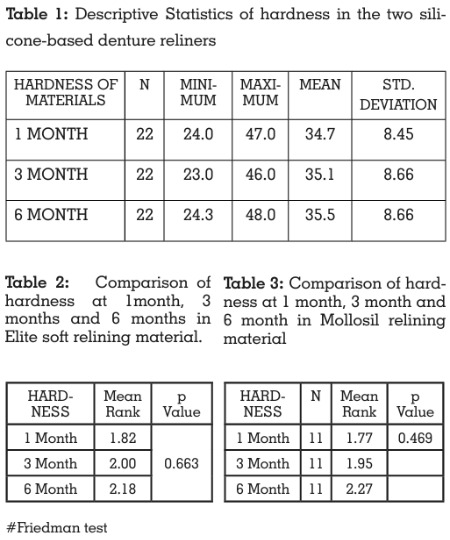
comparative in vitro study. Mean and standard
deviation among two silicone-based denture
reliners after storage in artificial saliva are
provided in Table 1. Elite relining material it
prove to have greater hardness than mollosil at
different time intervells of one month, 3 months
and 6 months (table 2 and 3).
Resilient denture liner is an interim (ethyl
methacrylate with phthalate plasticizers) or
definitive (processed silicone) liner of the
intaglio surface of a removable complete
denture, removable partial denture, or intraoral
maxillofacial prosthesis- GPT 911 As long as material is soft and resilient it will have a
rehabilitating effect of basal structures that has
traumatized, irritated, deformed or abused. Some
soft lining materials are not stable in aqueous
conditions such as oral cavity. This is true for
acrylic based soft lining materials containing
plasticizer which will leach out and cause the
lining to harden limiting its usefulness. Silicone
rubber material are most often been reported to
retain their hardness overtime for long.12 Stability
of hardness during use is a desirable feature of
long term soft denture liner (LTSDL) materials
because any increase in hardness can worsen
the distribution of the masticatory load and
lower the absorption of elastic energy, which is
transmitted onto the mucosal membrane under
dentures, thereby exacerbating the clinical
problems experienced by patients.
In case of increase in hardness of resilient
denture liners it may be a result of ongoing
polymerization and an increasing number of
cross-linking bonds between polymer chains.
Their initial hardness ranges between 25 and 50
degrees Sh A, and should not exceed 55 degrees
Sh A 28 days after the denture is relined.9
Here in this in vitro study we compared the change
in hardness of two silicone based reliners at 1
month, 3 months and 6 months. Properties were
evaluated at 1st, 3rd and 6th month to study the
change in properties overtime. Artificial saliva
was used to simulate the oral environment.
When the hardness of Elite soft relining material
was compared with Mollosil after storage in
artificial saliva at different time period; Elite
shows more hardness than Mollosil but the
hardness was within the required limits of LTSDL.
The comparison of hardness at 1 month, 3 month
and 6 month of both Elite and Mollosil shows
that there is no overall statistically significant
difference (p >0.005). This shows that there is no
change in hardness or loss of softness in Elite and Mollosil relining materials. This property of
stability in hardness over time is s beneficiary
property for a LTSDL for its use for a long time.
Future Perspective: An in vivo study on complete
denture patients wearing dentures relined with
different denture relining material would give a
better result.
Within the limitations of this study; following conclusions were drawn: