

Vaginal stents are most widely employed in the management of maintaining the patency of neovagina in patients with Mayer-Rokitansky-Küster-Hauser (MRKH) syndrome. Although several methods are available for the fabrication of vaginal stents, hardly any techniques are described in the literature to date to make the vaginal stent prosthesis hollow. This article presents a novel simple and cost-effective technique for fabricating custom hollow vaginal stent prostheses for patients with MKRH syndrome. This dental technique offers a convenient removable treatment option for maintaining the patency of the neovagina and is a very straightforward, reasonably simple, and cost-effective method for making vaginal stents.
Key words: Mullerian aplasia, stents, vagina
Mayer-Rokitansky-Küster-Hauser (MRKH)
syndrome is a congenital disorder in women
characterized by agenesis or aplasia of the uterus and upper part of the vagina1–3.
The
management of vaginal agenesis includes the
creation of a neovagina either by surgical or non-surgical approaches4
. Vaginal dilation created
by non-surgical methods is considered the first
line of management before the commencement
of any surgical intervention1. Frank’s method and
Ingram’s method are the two most common non-invasive vaginal dilation methods4. The most
commonly used method is Frank’s method where
progressive dilators are manually placed on the
vaginal apex1. Vaginal dilators are also used
postoperatively to maintain the width and depth
of the neovagina, prevent neovagianl contraction
or shrinkage, and serve as a hemostat as well5.
Maxillofacial prostheses and the materials
used in their construction have today provided
prosthodontists with a wide range of options to
serve humanity and assist our colleagues in the
fields of medicine, surgery, and allied specialties.
Prosthetic materials such as acrylic or acrylic
stents lined with silicones are widely used for
the fabrication of vaginal dilators5–7”. These dilators can be made hollow in order to reduce
the weight of the prosthesis thereby providing
patient comfort. This article describes a novel
simple technique for fabricating custom hollow
acrylic surgical stent for patients with Mayer-Rokitansky-Kuster-Hauser (MRKH) syndrome.
The patient’s privacy was not violated and
informed consent for publication was obtained
from the patient.
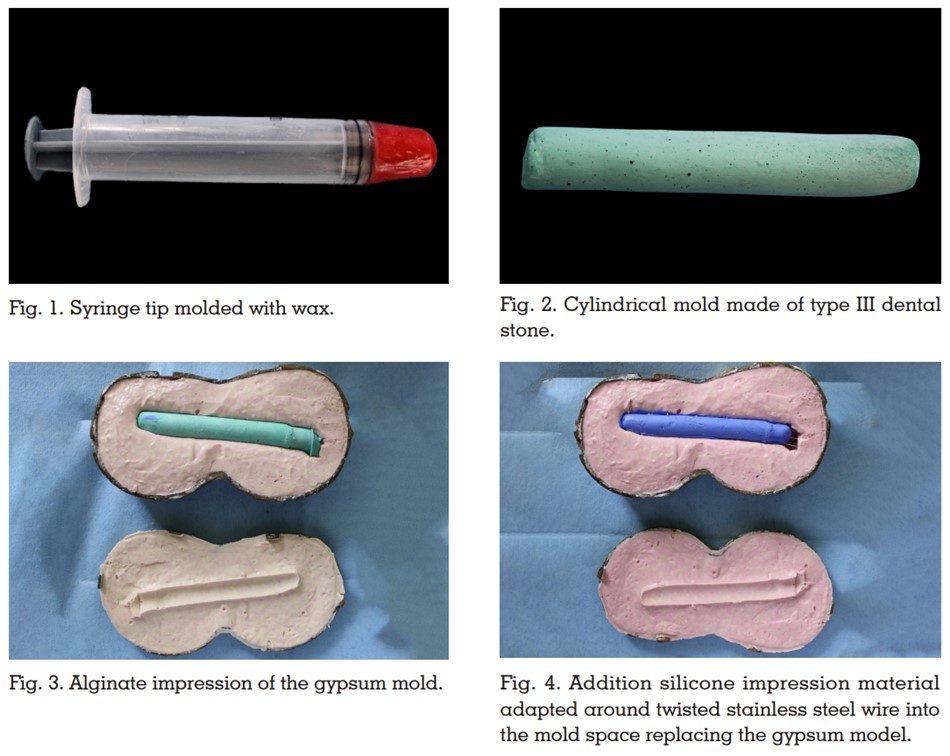
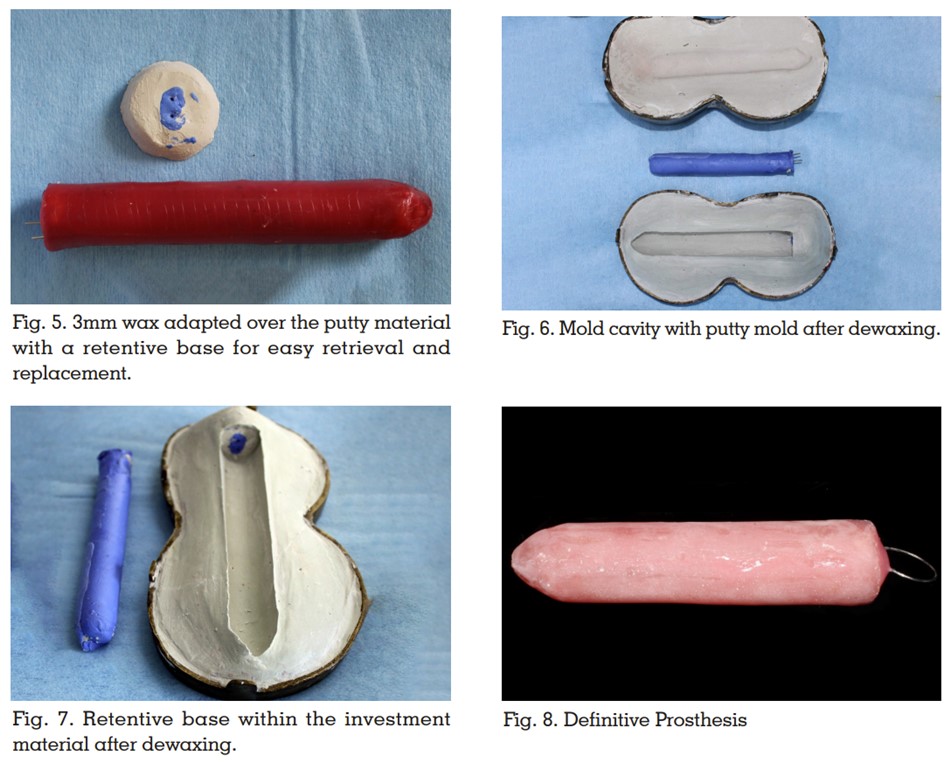
A comprehensive literature review has been
conducted by Callens et al. regarding the
management of vaginal agenesis and justified
vaginal dilators as the first line of treatment8.
Vaginal dilators are indicated as a non-surgical intervention method only when the
vaginal dimple is deep enough (2–4 cm)5.
Postoperatively, these vaginal stents are used
to preserve vaginal width and depth, as well as
to stop neovaginal stricture and contraction5.
Customized vaginal stents or dilators offer great
advantages compared to prefabricated ones
as it is economical, posses adequate strength
and durability9. The hollowed design reduces
the weight of the prosthesis making it more
comfortable for the patient. Moreover, the heat
activated acrylic resin material eliminates the
possibility of fungal infections as reported with
silicone materials5. The putty mold employed in
this technique for hollowing the prosthesis can
be effortlessly removed if fabricated without any
undercuts. A uniform and adequate thickness of material can be ensured all around the hollow
cavity with this technique. Low compliance from
the patient side, the time required to achieve
satisfactory result and initial discomfort are the
possible limitations.
The technique for fabrication of a custom-made hollow acrylic vaginal stent for patients
with Mayer-Rokitansky-Küster-Hauser (MRKH)
syndrome offers a convenient removable
treatment option for maintaining the patency
of the neovagina and is a very straightforward,
reasonably simple, cost-effective method for
making vaginal stents.