

Dentistry today, focuses not only on the prevention and treatment of disease but also on meeting the demands for better esthetics. Therefore, it has evolved from a creative to creative science in a short span. Due to the increase in importance and attention towards esthetics, the demand for metal free prosthesis is on a verge of increase. This article will review all the materials on the progress in dental materials owing to increase in demand for aesthetic.
Key words: Metal- free, esthetics, advances.
The field of dentistry is known for meeting the
requirements of patients by offering dental
restorations and prosthesis such as inlays,
onlays, crowns, fixed partial dentures (FPDs), and
removable dentures, to meet patients’ needs and
maintain their health. During the 20th century, both
dental materials and dental devices progressed
remarkably.1
Owing to the increased demand for
safe and esthetically pleasing dental materials,
new high strength Metal free materials have been
recently introduced.
Biomaterials for dental use are classified into
metal, ceramics, synthetic polymer and composite
materials. For dental prosthesis, previous ceramics
and resin were brittle, and the use of these alone
for restoration and dental prosthesis preparation
was limited due to the problem of the materials
strength. Thus, metal has been frequently used;
prioritizing mechanical strength over esthetics, but
demands for metal-free restoration has recently
increased due to esthetic problems of metal colour
penetration through the marginal gingiva and
gingival staining by metal, a problem of metal
allergy, and environmental protection concerning
rare metals.2
This review outlines the developments and progress
in dental materials over the past decade which
has lead to the evolution of metal free prosthesis
in complete dentures, fixed partial dentures,
removable partial dentures, implantology and
maxillofacial prosthesis.
In ancient time metal denture bases were used
but these dentures have heavy weight and
esthetically poor appearance that’s why a newer
material called PMMA (Polymethyl methacrylate) used for fabrication of denture. The mechanical
properties of PMMA are significantly enhanced by
the incorporation of Glass fiber. Silane coupling
agents play a central role in improving bonding
between fillers and the resin matrix, and they
subsequently improved the resin’s properties.3
The fabrication of complete dentures using a
conventional method associated with certain
problems. To avoid this, computer-aided design/
computer-aided manufacturing (CAD/CAM)
system have been successfully introduced into
restorative dentistry and maxillofacial technology
to simplify the fabrication procedure and resolve
the associated problems.4-8
Panasonic Corporation of Japan presented, a
composite material comprised of zirconia and
alumina using ceria as a stabilizing material i.e.
NANOZR, and acquired pharmaceutical approval
in October 2006.2
Since it has a marked mechanical strength, and
long-term stability in the mouth, clinical application
for fixed prosthesis and dental implants has been progressing.9,10,11 The load-bearing ability of Yttria
partially stabilized tetragonal zirconia (Y-TZP)
has been shown to be equivalent to that of Co-Cr alloy,12 and NANOZR may also be applicable
for denture base material substituting for metal
because its mechanical strength is greater than
that of Y-TZP.

Ceramics have domain the field of dentistry for
the past 200 years.
Porcelain presents with poor mechanical properties
& has relatively low tensile strength, it is therefore
generally fused to a metal substrate to increase
its resistance to fracture.13 However, this metal
base creates metal ion discolorations that may
affect the aesthetics of the porcelain reducing
light transmission through the porcelain. Allergic
reactions and sensitivity to various metals is seen
in some patients. These disadvantages, led to
the development of new all-ceramic (metal free
ceramic) systems that do not require metal.14
Introduction of IPS EMPRESS 2, the metal free ceramic systems, resulted in a long lasting metal
free ceramic restoration.
CAD-CAM with its advancements occasioned
in the restoration with better esthetics, strength,
and ease of fabrication in single visit. In CAD/
CAM system the occlusion with the opposing tooth
requires manual refinement. With the advent of
newer software and advancement in systems,
this shortcoming is expected to be solved in the
near future.14
The most frequently used zirconia-containing
ceramic systems presently accessible in dentistry
are- yttrium cation-doped tetragonal zirconia
polycrystals (3Y-TZP), magnesium cation-doped
partially stabilized zirconia (Mg-PSZ) and zirconia-toughened alumina (ZTA) 15,16,17.
Crowns with zirconia core materials have higher
mechanical properties than other metal-free
restorations, Yttrium-oxide is added to pure
zirconia to control the volume expansion and
to stabilize it in the tetragonal phase, at room temperature.18 Yttrium-oxide partially stabilized
Zirconia (Y-TZP) has mechanical properties with
a flexural strength of 900 – 1200 MPa19 and high
fracture toughness, making it suitable for anterior
and posterior crowns as well as for long-span fixed
partial dentures.20
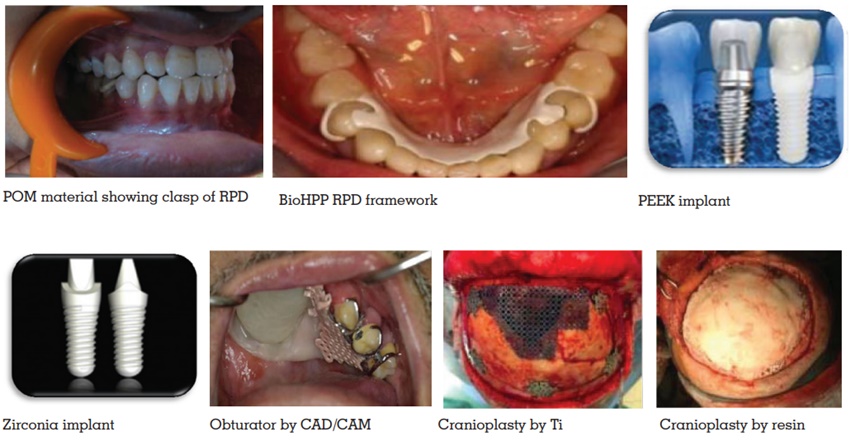
Dental prosthesis produces denture esthetics
that affects the beauty and attractiveness of the
person.21 Removable partial dentures (RPDs)
are the widely accepted treatment of choice for
most cases as it is both effective, affordable and
best treatment option for partial edentulism22 but
patients are concerned about the metal exposure
in cast partial dentures and hence worried about
the esthetic appearance.23,24 The traditional use
of the conventional metal clasps such as cobalt-chromium (Co-Cr), gold, stainless steel, and
titanium gives poor esthetic appearance due
to display in the oral cavity which hampers the
patient’s comfort.
Therefore a thermoplastic resin, Acetal resin
(polyoxymethylene [POM]), may be used as
an substitute clasp material. An unbreakable
thermoplastic resin, Acetal, was first proposed for
RPD material, in 1971. These injection moulded
resins were promoted mainly on its ability for
superior esthetics, which allowed the clasps to
better match the colour of abutment tooth.25
Thermoplastic materials were introduced in clinical
practice due to an aesthetically unacceptable
display of metal clasps, increased prosthesis
weight, the potential for metallic taste, and allergic
reactions to metals.26,27,28
PEEK permits RPD fabrication with metal-free
esthetic clasps and occlusal rests with better
occlusal stability owing to its white colour and
high strength.29
As an alternative RDP framework material,
a modified PEEK high performance polymer
(BioHPP) combined with acrylic denture teeth
and conventional heat-cured denture base acrylic
resin was used. BioHPP permits the fabrication of
metal-free clasps and occlusal rests, providing
occlusal stability and metal-free aesthetics due
to its white colour and high strength.29
Inorder to replace missing teeth dental implants
are used. For this, Brånemark introduced Titanium
(Ti) and its alloys as dental implants at the
end of the 1960s.30 Ti materials possess good
physicochemical characteristics, mechanical
properties and biocompatibility.31,32 Ti materials
have an elastic modulus higher than that of bone
(titanium: 110 GPa; cortical bone: 14 GPa), and
the difference may result in inadequate stress-shielding, bone resorption, and implant fracture.33,34
Occasional metal hypersensitivity and allergies,
surface degradation and contamination related
to peri-implantitis, and scattered radiation are the
clinical problems accompanying Ti materials.35
The Ti materials due to its metallic appearance
compromises highly aesthetic restorations. There
have been a lot of researches to develop substitutes
for Ti dental implants, such as zirconia36,37, which
has a high elastic modulus and low temperature
degradation.38,39 Polymeric compounds, such as
polyetheretherketone (PEEK), which is a semi
crystalline linear polycyclic thermoplastic that
was developed in 197840.
Wolff’s Law says that the bone remodels according
to the load that has been applied to it. Due to
shielding of normal loads by the implant there is
reduction in volume of the bone around implant
known as stress shielding. Finite-element analysis
(FEA) of carbon-fiber reinforced PEEK (CFR-PEEK)
implants suggested that they could induce lesser
stress shielding than titanium41.
The mechanical and physical properties of PEEK
are similar to bone and dentin, so it can be used
for a number of applications in dentistry including
dental implants. Here the challenge is faced while
increasing the bioactivity of PEEK dental implants
without affecting their mechanical properties.
It is an attractive material for producing CAD-CAM fixed and removable prosthesis compared
to materials such as acrylic. Further research
and clinical trials are required to explore this
material and possible modifications for further
dental application.42
Recently, high strength zirconia ceramics have
acquired a place of attraction as new materials
for dental implants. They are inert in the body
and exhibit minimal ion release. Owing to its
higher fracture resilience and flexural strength,
Yttrium-stabilized tetragonal zirconia polycrystals
appear to offer advantages over aluminium oxide
for dental implants.43,44
The inflammatory response and bone resorption
induced by ceramic particles are less than those
induced by titanium particles which suggest its
biocompatibility.45,46
Its the artificial device used to replace missing
facial or oral structures. Now a days CAD CAM
device is used for this.
Advantages of using CAD / CAM are:
The viable options option for less tissue irritation and more patient comfort are the intra oral scanning of a hemi maxillectomy patient and the implementation of CAD/CAM techniques for obturator fabrication.48 Cranioplasties have been performed since the early 1950s49. Acrylic resin materials form an alternative to bone substitutes in dentistry. Due to the properties like dimensionally stability, nonconductivity and economical, acrylic resins are used in implant dentistry.50 Acrylic resin has some advantages over metal substances; it is easy to shape, lighter in weight, radiates less heat, and radiolucent.51,52
Keeping in mind the various hazards of using
metals as prosthetic materials and the awareness
and demand for aesthetics has lead to the
evolution of metal-free prosthesis which will soon
be the future of dental prosthesis. An adequate
knowledge about the same is essential amongst
the practitioners in order to bring them in practice
unlike other conventional materials.